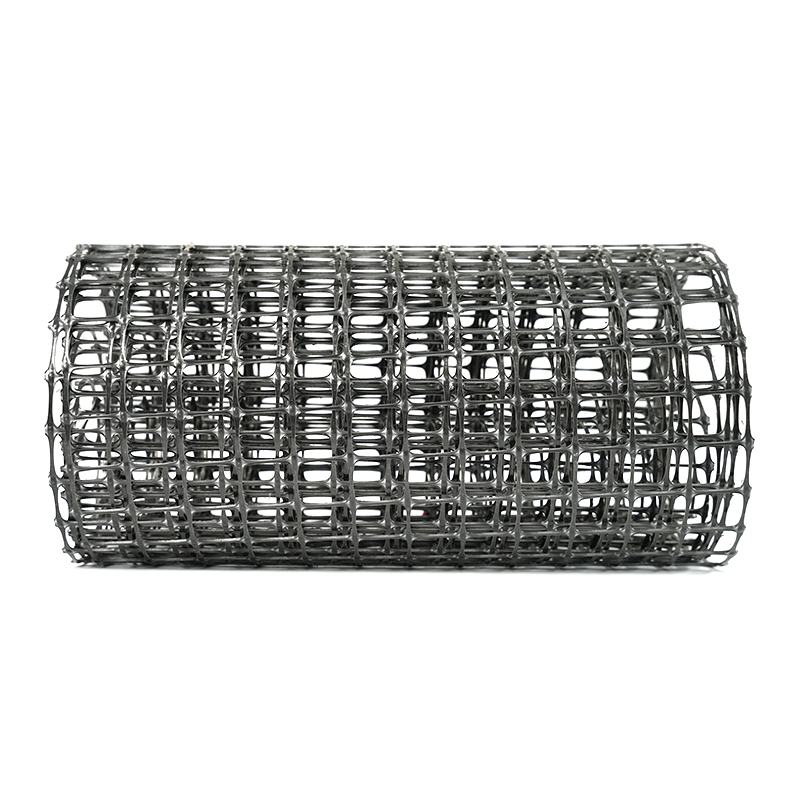
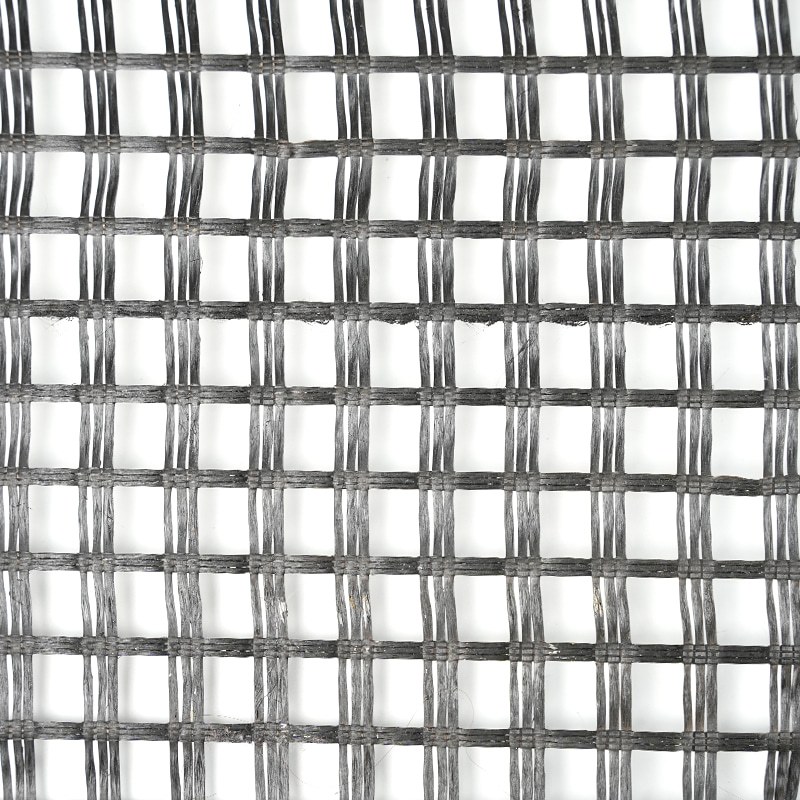
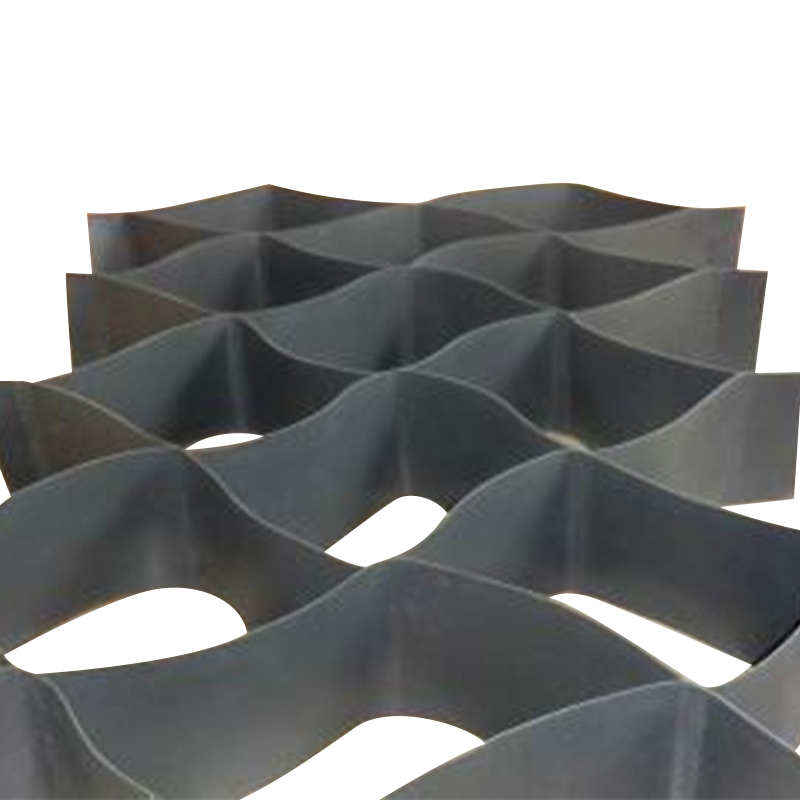
Main Applications of Geogrids
1. Roadbed and Pavement Reinforcement: Geogrids laid in the roadbed of highways, municipal roads, railways, and airport runways can significantly increase bearing capacity, distribute loads, reduce settlement, and extend service life.
2. Preventing Roadbed Material Loss: The mesh of the geogrid interlocks with the soil, inhibiting lateral movement and preventing soil loss, cracks, and rutting.
3. Slope and Embankment Reinforcement: Geogrids used in embankments, riverbanks, slopes, and slope protection projects can increase the structure's self-supporting capacity, reduce earth pressure, and expedite construction.
4. Retaining Wall Reinforcement: Geogrids placed in the backfill behind retaining walls can enhance the fill's self-stability and reduce the stress on the wall, thereby reducing the design thickness and maintenance costs of the retaining wall. 5. Soft Soil Foundation and Mine Support: In weak soils, mine tunnels, abandoned landfills, and other locations requiring increased pullout and compressive strength, geogrids provide high-tensile, low-elongation reinforcement.
6. Asphalt or Cement Pavement Reinforcement: Adding geogrids to the base of asphalt or cement pavements can reduce rutting depth, delay cracking, and appropriately thin the pavement structure.
Do retaining walls require geogrids?
1. Technical Specifications and Practice: The "Technical Code for Building Retaining Walls" in China clearly states that geogrids are a common material for reinforced earth retaining walls, increasing the self-bearing capacity of the backfill and reducing earth pressure.
2. Scope of Application: Geogrids are recommended for reinforcement in weak soils, deep foundation pits, or retaining walls requiring long-term durability. However, in extremely soft clay or very thick cement-soil retaining walls, the specification recommends using geogrids with caution or adopting other reinforcement methods. 3. Effect evaluation: Studies have shown that retaining walls using geogrids can significantly improve overall stability, reduce maintenance costs, and have been successfully applied in a variety of projects (such as highways, railways, and dams).


 中文简体
中文简体 русский
русский عربى
عربى













