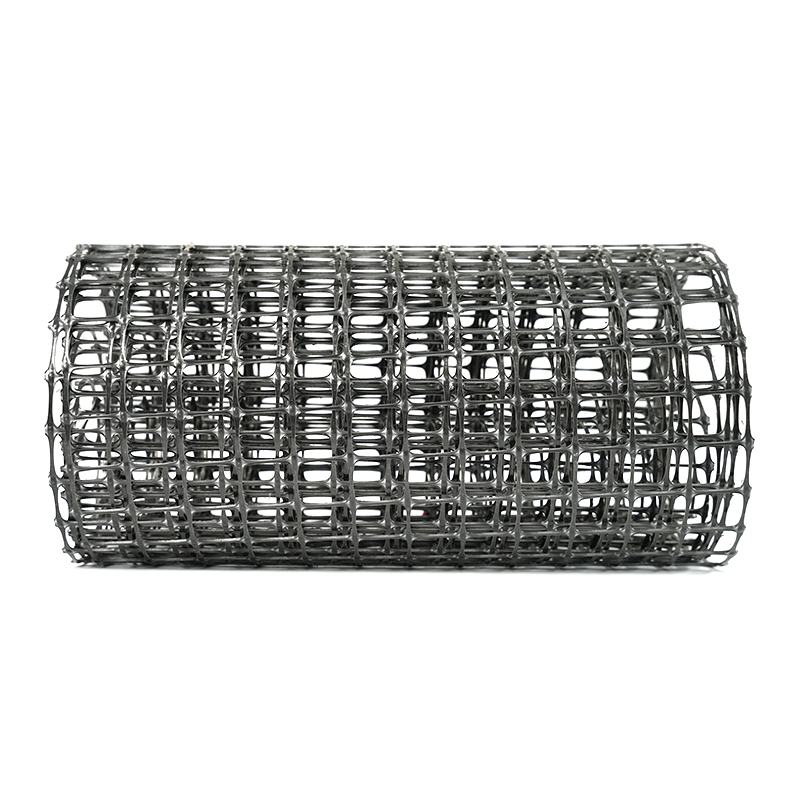
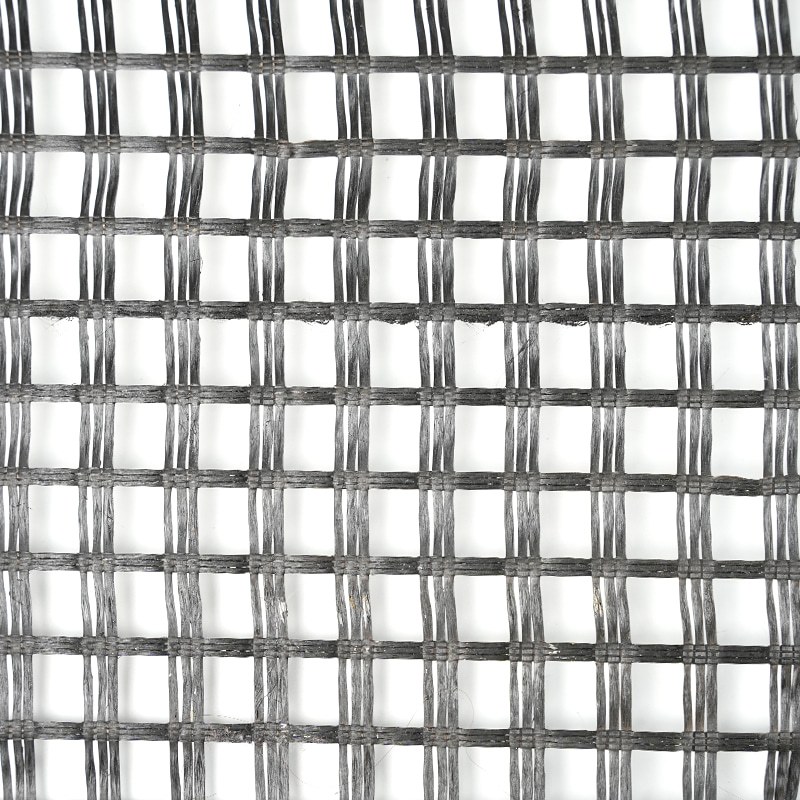
1. Materials and Structure: Fiberglass Geogrid uses high-strength, alkali-free glass fiber yarn, woven using advanced foreign warp knitting machines to form a directional warp-knitted skeleton. This fully utilizes the strength of the yarn, giving the mesh excellent tensile, tear, and creep resistance.
2. Surface Modification: High-quality modified asphalt is sprayed onto the surface of the fiber substrate to form an "asphalt grid." This composite layer protects the glass fiber and improves compatibility with asphalt mixtures, achieving good adhesion and barrier properties.
3. Mechanical Properties: The product possesses high tensile strength, low elongation (<3%), high-temperature durability, low-temperature shrinkage and crack resistance, and virtually no long-term creep, maintaining its shape and performance under harsh road load cycles.
4. Standards: Complies with the testing standards JT/T480-2002 and JTGE50-2006, the testing specifications for highway geosynthetics. All physical indicators have been verified by national authoritative testing institutions.
What are the typical applications of Fiberglass geogrid in road and foundation engineering?
1. Asphalt pavement reinforcement: Adding Fiberglass geogrid before laying asphalt pavement significantly improves the pavement's resistance to cracking, rutting, and thermal shrinkage, extending its service life. It is particularly suitable for high-traffic sections such as highways and urban arterial roads.
2. Cement concrete pavement reconstruction: Laying fiberglass geogrid on existing cement pavements can suppress reflective cracking caused by slab shrinkage and improve overall stiffness. It is commonly used in bridge decks, airport runways, and other projects requiring high durability.
3. Soft soil and foundation reinforcement: Placing Fiberglass geogrid in soft foundations or soft soil fill layers can evenly distribute the superstructure load, reduce settlement and uneven deformation, and improve overall bearing capacity. It is widely used in railway subgrades, dam slopes, and port reclamation projects.
4. Crack prevention in semi-rigid base layer: Adding fiberglass grid to the semi-rigid base layer of newly built roads can effectively prevent the base shrinkage cracks from being transmitted to the surface layer, playing a role in "delaying and mitigating" reflective cracks and improving the crack resistance of the overall structure.


 中文简体
中文简体 русский
русский عربى
عربى













